
Unlocking Material Performance: A Guide to Cross-Linking Agent Applications
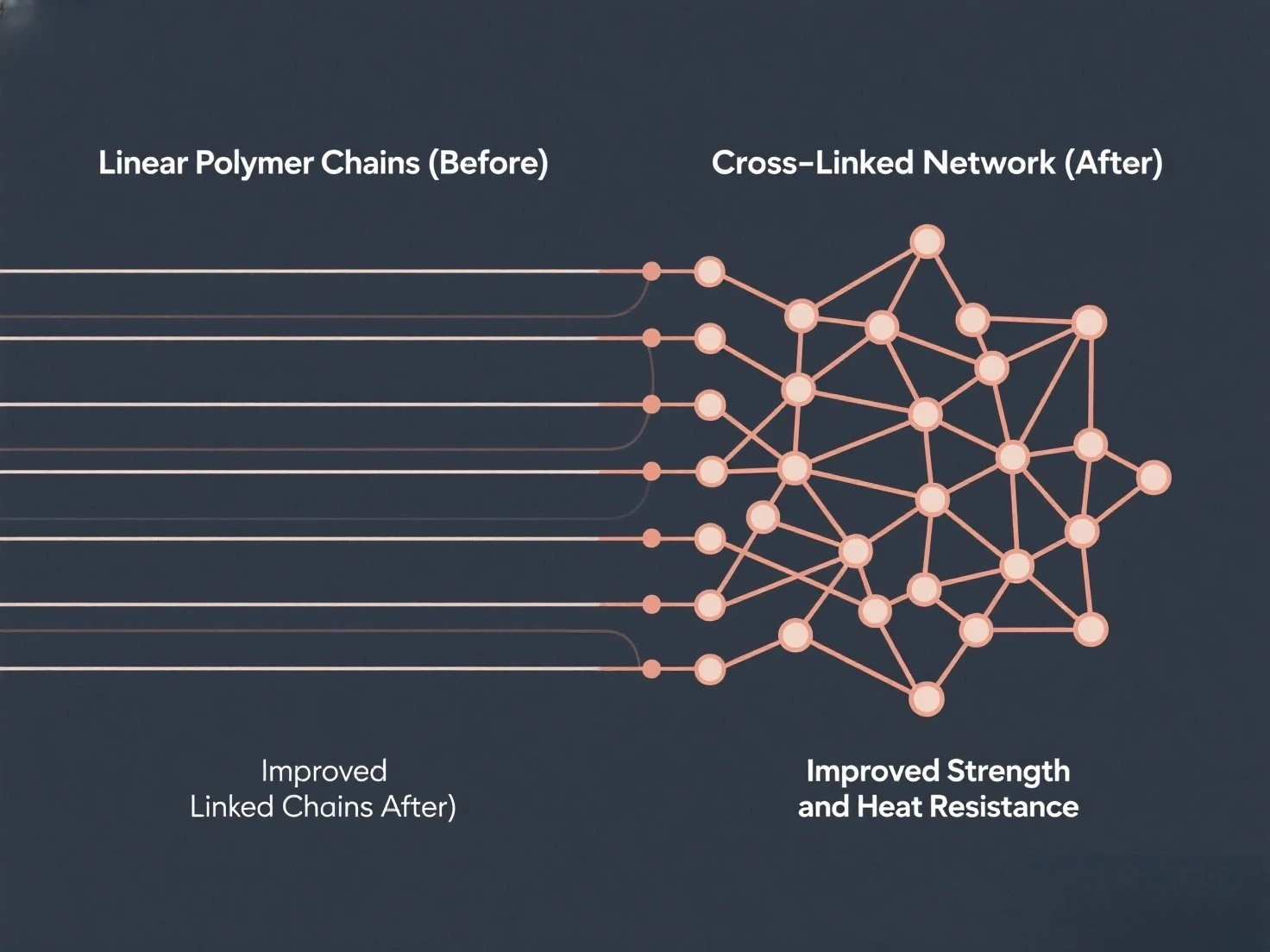
Have you ever wondered what gives modern materials their incredible strength, heat resistance, and durability? In many cases, the secret lies in a powerful but unseen component: the cross-linking agent. Also known as a bridging agent, a cross-linker is a substance that creates powerful bonds between linear molecules, transforming them into a robust, three-dimensional network.
This transformation dramatically enhances material properties. The impact of these agents is felt across a vast array of sectors, making them essential in the production of thermoplastics, specialty rubbers, resins, advanced electronics, cutting-edge medicine, and even the food industry. Let’s explore the pivotal role cross-linking agents play in these key areas.
Revolutionizing Thermoplastics and Resins
In the world of polymers, performance is everything. Cross-linking agents are instrumental in elevating the properties of common plastics and resins from standard to high-performance.
Enhancing Thermoplastic Durability
For widely used materials like polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride (PVC), adding a small amount of a cross-linking agent—typically just 1-3%—can yield remarkable results. This simple addition can significantly boost heat resistance, improve mechanical strength, and increase flame retardancy without altering the product’s shape or integrity.
- Illustrative Example: A manufacturer of high-pressure pipes uses cross-linked polyethylene (PEX) instead of standard polyethylene. The cross-linking process creates a stronger material that can withstand higher temperatures and pressures, preventing leaks and extending the service life of the plumbing system.
Advancing Resin Technology
For materials like acrylic and styrene resins, a minimal amount of a cross-linker can lead to significant quality improvements. This is particularly evident in the production of new ion exchange resins, where cross-linking creates a stable, high-performance structure. Furthermore, in applications using epoxy resins and DAP resins, these agents are key to improving thermal stability, adhesion, and mechanical strength.
Boosting Strength in Specialty Rubbers
Cross-linking is a cornerstone of the rubber industry, particularly for high-performance elastomers. In materials like ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) and fluoroelastomers (FKM), cross-linking agents are used to:
- Accelerate the vulcanization (curing) process.
- Significantly increase tensile strength and durability.
- Improve resistance to abrasion and chemical corrosion.
The typical dosage in these applications ranges from 0.5% to 4%. According to industry reports, properly cross-linked specialty rubbers can see a service life extension of over 50% in demanding automotive or industrial environments.
Powering the Future of Electronics
How do sensitive electronic components survive in harsh environments? Cross-linking agents provide the answer. They act as powerful protective agents, shielding metallic and polymer components from heat, radiation, and weathering.
When added to the materials used for circuit boards and high-voltage insulating materials, cross-linkers create a shield that enhances insulation, protects against radiation interference, and ensures the components can operate reliably at elevated temperatures.
Innovations in Medicine and the Food Industry
The influence of cross-linking agents extends into highly regulated and sensitive fields, improving both health outcomes and food quality.
Biocompatible Materials in Medicine
In the medical field, biocompatibility and durability are non-negotiable. Cross-linkers are essential in creating the advanced biomaterials used in:
- Artificial joints, where they provide the strength and wear resistance needed for long-term use.
- Implantable stents, offering structural integrity and flexibility.
- Dental restorative materials, ensuring long-lasting and safe fillings and crowns.
Enhancing Quality in the Food Industry
As regulated food additives, cross-linking agents are used to modify and improve the physical properties of food products. They can act as stabilizers, thickeners, or gelling agents, enhancing texture, moisture retention, and overall quality, thereby increasing both shelf life and nutritional value.

From strengthening everyday plastics to enabling life-saving medical devices, cross-linking agents are fundamental to modern material science. Their ability to forge robust molecular networks allows us to push the boundaries of performance across countless industries.
The world of cross-linking agents is vast and complex, with specific solutions required for different materials and applications. Are you unsure which agent is right for your process or need help navigating CAS numbers and product specifications?
Contact us today for a consultation. Our experts are here to help you select the perfect cross-linking agent to unlock the full potential of your materials.
Click to view our catalog.
